Hemp Complex - more than CBD oil!
Terpene compounds found in Hemp Complex
Terpenes benefits in Hemp Complex raw oil:
Each hemp strain has a unique terpene profile, with a distinguished structure and concentration of terpenes. Thanks to independent laboratories, universities and privately funded organizations, the world sees new research results from all over the world on certain components of the hemp plant almost every single day. The legalization of medical marijuana and hemp has provided researchers around the world with the opportunity to participate in various research programs and studies to share their results with the world. At the end of the 1990s, due to international legislation, it was very difficult to conduct Cannabis research. Fortunately, the legislation has relaxed in this field, thus research results from the last 30 years brought breakthrough successes. You can read more about the terpenes found in the Hemp Complex here!
The main terpenes found in Hemp Complex raw CBDA - CBD oil
The main terpenes found in CbdBase’s raw Hemp Complex CBDA – CBD oil.
The numeric values are referencing mg/g and percentages by mass.
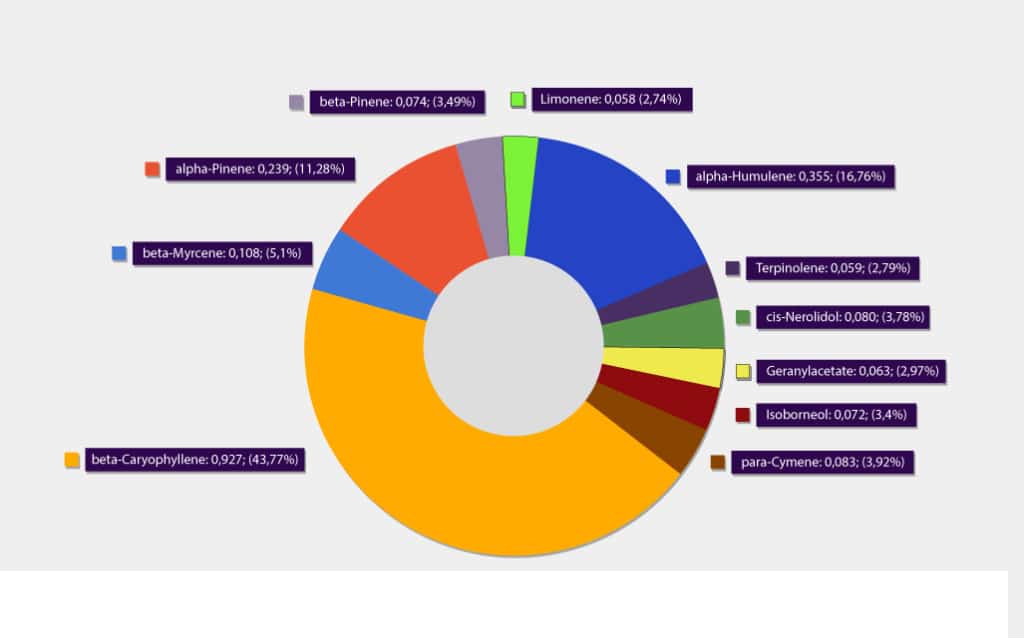
About the terpenes benefits you can read here:
Myrcene (ß-Myrcene)

Chemical formula: C10H16
Molar mass: 136.23404 g/mol
Decarboxilation Point: 115-145°C (239°F and 293°F)
Boiling point: 168°C (334°F)
Steam pressure: 7.00 mmHg (20°C)
Myrcene is a monoterpene, molecularly the smallest of terpenes and is found in very high concentrations in basil, hops, mango, lemongrass, thyme, eucalyptus and cannabis. Myrcene terpene characteristically smells earthy, fruity clove-like, however it can be very pungent in higher concentrations.
Its name came from a herb called Myrcia sphaerocarpa, which contains a very large amount of myrcene and has been used as a remedy for diabetes, dysentery, diarrhea and hypertension for centuries. In a 1997 study conducted in Switzerland, 16 terpenes were analyzed in different subspecies of Cannabis and found that myrcene was the most abundant among them (in addition to pinene, limonene, carene, humulene, bergamotene, terpinolene, and caryophyllene). Myrcene alters the permeability of cell membranes, allowing greater absorption of cannabinoids in the brain.
Myrcene has many known therapeutic effects
Myrcene is one of the main components of menthol and lemon balm, and arguably the most cited terpene. Myrcene is known to have many therapeutic effects, including muscle relaxing and pain relief. In addition, it is an antidepressant and anti-inflammatory agent. Like another terpene, limonene, it affects the permeability of cell membranes, meaning it regulates the effects of other terpenes and cannabinoids by increasing or buffering them.
Myrcene also has an antimicrobial, antiseptic, antioxidant and anticarcinogen effect. It helps other cannabinoids and terpenes pass through the cell membrane, allowing more cannabinoids to reach brain cells, thereby increasing the effectiveness of biologically active compounds within the CBD oils. This is a perfect example of the so-called “Entourage effect”, in which terpenes and cannabinoids work together to synergistically increase each therapeutic effect that could not be achieved with a single cannabinoid or a terpene.
Myrcene terpene also demonstrably slows down the growth of bacteria, inhibits cell mutations (which plays a role in fighting cancer), suppresses muscle spasms (making it an effective tool against epilepsy and dystonia) and it can be even useful for people suffering from psychosis due to its calming effect.
Medicinal applications of myrcene
Analgesic – Relieves pain – in synergy with cannabinoids.
Antibacterial – It destroys bacteria.
Antidiabetic – Helps mitigate the symptoms of diabetes.
Anti-inflammatory – Reduces inflammation within the body – in synergy with cannabinoids.
Anti-insomnia/Anaesthetic effect – It promotes sleep – in synergy with cannabinoids.
Antiproliferative/Antimutogene Inhibits cell mutations, including cancer cells, in synergy with CBD and CBG.
Antipsychotic – Its sedative effect relieves the symptoms of psychosis – in synergy with CBD and linalool.
Antispasmodic – Suppresses muscle spasms – in synergy with THCA and CBD.
Caryophyllene (β-Caryophyllene)

Chemical formula: C15H24
Molar mass: 204.35106 g/mol
Boiling point: 160°C (320°F)
Caryopyllene is the primary terpene contributing to the spiciness of black pepper and is also one of the main volatile substances of cloves, hops, rosemary, basil and Cannabis. It is also an ingredient of Thai basil and cinnamon. There are two main forms, beta-caryophyllene or β-caryophyllene (abbreviated as BCP) and trans-caryophyllene or TC. Caryophyllene is a sesquiterpene formed by three isoprene units, therefore it is molecularly larger than monoterpenes such as pinene, limonene and myrcene. The latter are made up of only two isoprene units. What makes caryophllene chemically unique is that it contains a cyclobutane ring, which is rare in nature. Some cyclobutanes are already being used for medical purposes such as the chemotherapy drug carboplatin.
It has many medicinal effects
Caryophyllene is unique not only for containing cyclobutane but also for containing both terpene and “dietary cannabinoids“, a food substance that acts as a cannabinoid and binds to the CB2 receptor. Cannabinoids are terpenephenol compounds, belonging to the subclasses of terpenes. Since cannabinoids and terpenes are related compounds, it is not surprising that terpenes activate endocannabinoid receptors in the body.
The same 2008 study, which first identified caryophyllene as a cannabinoid, also reveales its numereous medicinal effects, including antioxidant, anti–inflammatory, anti–cancer and local anesthetic effects. Some sources believe that BCP may be so effective, it could even compromise well-marketed drugs and synthetic cannabinoids under development.
Medicinal applications of caryopyllene
Painkiller – Relieves pain – in synergy with THC and CBD.
Antibacterial – It destroys bacteria.
Antidepressant – Relieves symptoms of depression – in synergy with THC.
Anti-inflammatory – Reduces inflammation in the body.
Antiproliferative – Inhibits the growth of cancer cells.
Antioxidant – Prevents damage caused by oxidation (free radicals).
Anxiolitic – Relieves anxiety.
Neuroprotective – Protects against damage in the nervous system and brain.
Caryophyllene is the only terpene known to interact with the endocannabinoid system, and its attachment to the CB2 receptor produces an anti-inflammatory effect in the body. When used in conjunction with cannabinoids, especially CBD, it has been shown to reduce chronic pain. The smell of caryophyllene is peppery or spicy.
Humulene

Chemical formula: C15H24
Molar mass: 104.35106 g/mol
Boiling point: 198°C (388°F)
Steam pressure: 0.01 mmHg (25°C)
Humulene is one of the most important terpenes in Humulus lupulus – ordinary hops – where its name derives from. It also occurs in hemp, sage and ginseng. Humulene is commonly referenced as α-humulene or α-caryophyllene. Although humulene has strong associations with β-caryophyllene, it has different characteristic properties. It is considered a dietary cannabinoid. Similairly to caryophyllene, humulene contains one sesquiterpene and three isoprene units, but does not have a cyclobutane ring.
Medical applications of humulene
Strong anti-inflammatory and analgesic
Humulene is like most other cannabinoids and terpenes, that is, it is a powerful anti-inflammatory and analgesic. It also has anti-tumor properties. Humulene is unique because – like THCV – it acts as an appetite suppressant and promises to promote weight loss.
Medicinal use:
Painkiller – Relieves pain.
Antibacterial – Slows down the growth of bacteria.
Anti-inflammatory – Systematically reduces inflammation.
Anti-proliferation – Inhibits the growth of cancer cells.
Anorectic – Appetite suppressant, promotes weight loss.
source of terpene benefits:
http://theleafonline.com/
https://weedmaps.com
Limonene

Chemical formula: C10H16
Molar mass: 136.23404 g/mol
Boiling point: 176°C (349°F)
Steam pressure: 1.50 mmHg (25°C)
Limonene is a cyclic monoterpene with a pronounced citrus smell and aroma, slightly sweet, yet tart and bitter. Not surprisingly, limonene is most often found in high concentrations in citrus peels as well as in rosemary, juniper, and peppermint. Until now, research on the medicinal properties of limonene has focused mainly on d-limonene.
Varieties of cannabis containing limonene terpene
Cannabis varieties with a high content of limonene terpene have a strong citrus aroma, similar to oranges. Limonene promotes the absorption of other terpenes through the skin. The widely used limonene terpene is a common ingredient in perfumes, household cleaners, food and medicines. Limonene is a https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carvone – Preparation chemical precursor to the carvon terpenoid and could be related to α-pinene.
Limonene can have a number of medicinal effects, including the promotion of weight loss and healthy digestion, as well as preventing upset stomach. It has been shown to be an antifungal agent, so it can be used as a natural solution for the treatment of fungal infections. Limonene is effective in treating anxiety and depression. Most interestingly, limonene has shown to have the ability to stimulate the immune system, as well as an effective complementary therapeutic potential for tumor diseases. According to WebMD, limonene can block the processes involved in the development of cancer and it is able to destroy tumor cells.
Medicinal applications of limonene
Antidepressant – Relieves symptoms of depression – in synergy with CBD and CBG.
Antifungal – Inhibits the growth of fungi – in synergy with CBC and CBG.
Anti-inflammatory – Reduces inflammation in the body.
Anti-proliferative – Inhibits the growth of cancer cells – in synergy with THC, CBD and CBG.
Anxiolitic – Relieves anxiety – in synergy with CBD.
Gastro-oesophageal reflux – Reduces acid reflux.
Immunostimulant – Stimulates the immune system.
Nerolidole

Chemical formula: C15H26O
Molar mass: 222.37 g/mol
Boiling point: 122°C (252°F)
Nerolidole is considered one of the most beneficial terpenes with the most favorable properties, since it exerts a wide range of health-supporting effects on the body. Trans-nerolidole in herbs and spices is mainly known for its medicinal use.
This is a secondary terpene, which is a compound in lemon balm, tea tree, ginger, jasmine and certain types of hemp. It smells a little like jasmine and apples. Research is currently underway concerning its use as an anti-parasitic and antifungal agent.
Medicinal applications of nerolidole
Anti-parasitic – An externally applicable product that can penetrate the skin and thus treat leishmaniasis caused by the genus of triphanosomes, is currently undergoing scientific testing.
Babesia parasitic inhibitory effect
As above, it can be effectively used against the blood parasite responsible for babesia.
Fungicide effects
– The external treatment of skin fungus may prove effective by using transnerolidole.
Staphylococcus treatment
It can be effective in preventing and treating infections already resistant to other commonly used antibiotics in medicine. According to research, it literally works hand in hand with antibiotics to destroy infections.
Like most terpenes, trans-nerolidole is likely to have antifungal, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects and it works as an immune booster. As a result, this terpene can help prevent and treat heart disease and tumors, while also displaying analgesic effects.
Linalool (β–Linalool)

Chemical formula: C10H18O
Molar mass: 154.24932 g/mol
Boiling point: 198°C (388.4°F)
Linalool is a compound in more than 200 plant species; most commonly in lavender, but it is also a common terpene of the hemp plants. Plants containing linalool are often used in aromatherapy as a sleep-promoting agent and relaxant. They have been used to treat anxiety for thousands of years. Linalool plays a key role in the body’s production of vitamin E, so it is very important and essential for the healthy functioning of the body.
Medicinal applications of linalool
Painkiller – Relieves pain – in synergy with THC and CBD.
Antidepressant – Relieves symptoms of depression – in synergy with THC.
Antiepileptic – Reduces epileptic seizures and spasms – in synergy with CBD, THCV and CBDV.
Anti-inflammatory – Reduces inflammation in the body.
Antipsychotic – Its calming effect relieves the symptoms of psychosis.
Anxiolitic – Relieves anxiety – in synergy with CBD and CBG.
Anti-insomnia/Sleeping Effect – Promotes sleep – in synergy with THC and CBN.
Studies show that linalool can significantly reduce respiratory inflammation caused by smoking and potentially reverse the histopathological characteristics of Alzheimer’s disease.
Alpha-Cedrene

Chemical formula: C15H24
Molar mass: 204.357 g/mol
Boiling point: 261-262°C
Sesquiterpene has a fresh, delicately woody aroma, typically occurring in cedar essential oil. Cedrene is a very versatile terpene. Theere were studies on the antispasmodic and anti-tumor properties of cedrene-containing essential oils. These oils are effective mosquito repellents as well. In holistic medicine, cedar tree oil has a huge range of uses. According to some holistic health professionals, cedar tree oil can promote hair growth and stimulate the scalp through massage. It is used to cure acne, disinfect wounds and overcome “restless leg syndrome”.
Medicinal applications of alpha – cedrene
Anti-hemorrhagic effect: Although human research is still incomplete, practical experience shows that cedrene terpene has an effective astringent effect.
Antibacterial: A study claims that the combination of cedrol and cedrene in plants has antibacterial and antitumor effects. However, these effects were not observed in cedrene alone.
Anti-cancer effect: When examining the anti-tumor potential of cedrene, there is an outstanding study worth considering. It describes the destruction of tumor cells in human tissue, and opens up the possibility of how it can be used as a natural anti–cancer remedy.
Pinene

Chemical formula: C10H16
Molar mass: 136.23404 g/mol
Boiling point: 155°C (311°F)
It is the most common terpene in the world and usually occurs at higher concentrations in Cannabis sativa species. Pinene is also crucial for our body, as it forms the basis of biosynthesis of CB2 ligands in the endocannabinoid system.
In fact, there are two types of pinenes: alpha and beta-pinene. It occurs most often in pine trees and coniferous plants. Beta-pinene can also be found in various herbs such as dill, parsley, rosemary or basil.
Studies have shown that pinene has anti-inflammatory and bronchial dilating effects.
Research suggests that pinene has a bronchial dilating effect because it increases the air flow in the lungs, thus it can help with disorders such as asthma. Like many terpenes and cannabinoids, pinene has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, so it can be used for people with chronic pain. Pinene helps fight tumors by stimulating apoptosis and antiproliferation. Pinene has antioxidant properties, which are beneficial to the entire body.
Medicinal applications of pinene
Painkiller – Relieves pain.
Antibacterial – Slows down the growth of bacteria.
Anti-inflammatory – Reduces inflammation.
Anti-proliferation – Inhibits the growth of cancer cells.
Antioxidant – Prevents oxidation damage of other molecules in the body.
Borneole

Chemical formula: C10H18O
Molar mass: 154.24932 g/mol
Boiling point: 213°C (451°F)
Also known as bornan-2, this compound has a highly pervasive, cool, spicy-minty scent, occuring in rosemary and plants of the mint genus, among many others.
Borneole is a bicyclic monoterpene, hence it contains two isoprene rings, making it larger than monoterpenes such as limonene, yet it is smaller than sesquiterpenes such as caryophyllene. In addition to its many medicinal benefits, borneole is a natural insect repellent, so it can prevent the spread of diseases transmitted by mosquitoes, fleas and other insects.
Medicinal applications of borneole
Painkiller – Relieves pain.
Antibacterial – Destroys bacteria.
Fibrosis inhibitor – Balances the body’s response to injuries.
Fungicide effect – Inhibits the growth of fungi.
Anti-inflammatory – Reduces inflammation in the body.
Antioxidant – Prevents oxidation (free radicals) damage in synergy with THC and CBD.
Terpinolene (delta-terpinene)

Chemical formula: C10H16
Molar mass: 136.23404 g/mol
Boiling point: 183-220°C (361-428°F)
Terpinolene is a smokey or woody-scented terpene occuring in apples, caraway and tea tree. Another name for terpinolene is δ-terpinene or delta-terpinene.
Terpinolene is not an analgesic or an anti-inflammatory, which is surprising since most cannabinoids and terpenoids have these properties. Like most cannabinoids, it promotes the fight against tumors, and it has antifungal and anti-bacterial effects. Terpinolene is a sedative substance that can be useful in treating tumors, even when patients find it difficult to sleep. When used in conjunction with other terpenes or cannabinoids such as linalool and cannabinol, it effectively shows greater efficacy.
Medicinal applications
Antibacterial – Slows down the growth of bacteria.
Antifungal – Inhibits the growth of fungus.
Insomnia control – It promotes sleep.
Anti-proliferation – Inhibits the growth of cancer cells.
Antioxidant – Prevents oxidation damage in other molecules in the body.
Cymene

Chemical formula: C10H14
Molar mass: 134,222 g/mol−1
Boiling point: 177°C (351°F)
It is very common terpene with a wide variety of biological activities, namely antibacterial and antimicrobial effects. In addition to its presence in certain Cannabis strains, cymene occurs in more than 100 different plants such as anise, oregano, eucalyptus, coriander and geranium.
This aromatic organic compound is a component of many plant essential oils, including cumin and thyme. As a component of thyme oil, cymene shows antimicrobial activity. Animal studies have also proven the anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of cymene.
Medicinal applications of cymene
In addition to its aromatherapeutical benefits, cymene can help fight inflammation and tumors. So far, the results are encouraging in animal experiments.
Antibacterial and antimicrobial effect: One of the most characteristic properties of cymene is that it inhibits the growth of microbes. Thyme oil is a very common antimicrobial. This particular feature of cymene is significant from a food safety point of view, although its strong smell may limit its usability. With the increase in antibiotic-resistant infections, the natural antibacterial properties of cymene can be of great importance.
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic:
According to a 2013 study published in the Journal of Inflammation, cymene acts as an anti-inflammatory agent through many cellular information transmissions in the body. Inflammation is an important aspect of pain and another German study, the Journal for Nature Research, also confirmed its anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of on mice. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25856703/ Further research published in the journal Pharmaceutical Biology suggests that the body’s natural opioid system affects the success of cymene in relieving pain in animals.
Antioxidant and nerve protection agent:
Many diseases arise from the imbalanced proportion of free radicals in the body, and natural antioxidants are the antidote to maintaining this balance. Scientists in Brazil showed the antioxidant properties of cymene in 2015. A 2019 study published in the journal Fitoterapia confirmed these findings, and also showed that cymene can act as a nerve protector due to its antioxidant effect.
Antitumor effect:
Numerous studies prove the positive role of cymene in fighting tumors. Much of this research was carried out using human cells grown in laboratories. The researchers found that cymene inhibits the development of connective tissue tumors , ovarian cancer, lung cancer and other cancers. People often use cannabis as an alternative therapy in the fight against cancer, but much more research is necessary to further understand the role of cymene in this therapy.


