Flavins and flavonoids in the Hemp Complex product family Full spectrum raw CBGA - CBDA oils
Flavonoids are pigments responsible for the flavors and colors of plants, including cannabis.
Flavonoids are found in many foods and could be useful for treating chronic pain, cancer, Alzheimer’s Disease, and many other conditions. Turmeric latte, anyone? There are over 6,000 different types of flavonoids in the plant world which are classified into three main groups:
- Flavonoids
- Isoflavonoids
- Neoflavonoids
Flavonoids are further broken down into twelve separate categories:
- Anthocyanins
- Flavanones
- Flavanonols
- Flavans
- Isoflavonoids
- Isoflavones
- Isoflavanes
- Isoflavandiols
- Isoflavenes
- Coumestans
- Pterocarpans
Learn the role of each flavonoid in the cannabis plant in our comprehensive guide to these essential compounds.
First, flavonoids are essential for numerous plant functions, including reproduction and ultraviolet (UV) filtration. These key compounds also act as chemical messengers and physiological regulators. In short: flavonoids are essential for the plant’s survival and reproduction.
Beyond their role in the life cycle of a plant, flavonoids offer wide-ranging health benefits for people.
Each flavonoid offers health benefits, but these are some of the most common therapeutic uses for flavonoids:
- Protect your cells from damage (antioxidants)
- Fight disease-causing inflammation
- Improve cardiovascular function
- Prevent or decrease cognitive decline, including dementia
- Treat viral infections
- Reduce the risk of diabetes, cancer, and many other diseases
Flavonoids carry no known side effects. However, taking flavonoid supplements may pose certain risks, as can any other dietary supplement not regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Toxicity issues and drug interactions may arise from certain flavonoid supplements. It’s best to get your fill of these botanical compounds straight from the source: fruits, veggies, and herbs.
Cannabinoids, flavonoids, and terpenes/terpenoids interact together to produce unique physiological effects. Flavonoids can be used for several ailments at different concentrations and dosages via interaction with our endocannabinoid system (ECS).
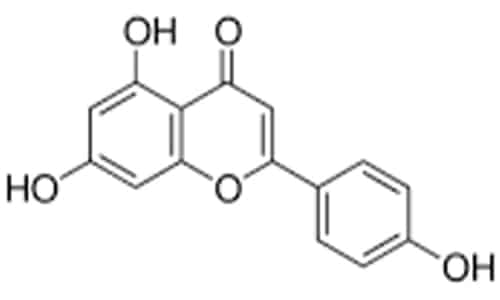
Apigenin
Parsley, celery and chamomile are the most well-known sources of apigenin, but they are inside many other fruits and vegetables as well. Apigenin approximately binds to 160 proteins in the human body. Researchers observed that apigenin by attaching to the hnRNPA2 protein, restores apoptosis in breast cancer cells, causing the death of tumor cells and/or the cells becoming much more receptible to chemotherapy. Its beneficial effect not only limits itself to the destruction of cancer, since apigenin also has an anti-inflammatory effect. Alpigenin may have numerous other, so far undiscovered physiologically beneficial properties. These could very well possess significant synergistic potential.
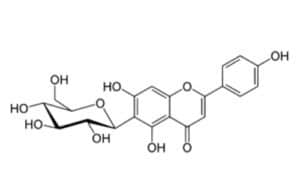
Isovitexin
Isotivexin (or homovitexin, also known as saponaretin) belong to the group of flavones. Apigenin-8-C-glucoside flavone, to be exact. It is inside passionflower, Cannabis and acai palm. Vitexin and isotvitexin are active components of many traditional Chinese drugs. Vitexin has recently received increased attention due to its extensive pharmacological effects. These includine antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory and nerve-protecting effects. Isofexin (apigenin-6-C-glucoside) is the isomer of vitexin. It is usually isolated together with vitexin and also exhibits a variety of biological activity. Recent research suggests that vitexin and isotivexin may be potential substances to substitute traditional drug therapy for the treatment of many diseases. Possibly they can complement alternative therapies for chronic diseases.
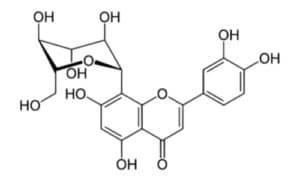
Orientin
Orientin is a flavonoid-like compound, which is a luteolin 8-C glucoside. It is inside passionflower, Acaí palm, buckwheat seeds, Brussels sprouts,and millet. It is a significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory, antiviral and antibacterial agent. Moreover, it is a vasodilator and cardioprotective, radioprotective (protects from harmful radiation) anti-depressant and protects the nervous system.
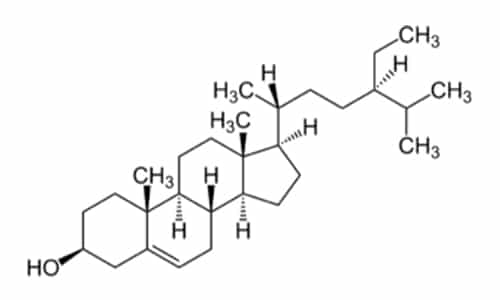
Beta-Sitosterol
β sitosterol (beta-sitostererin) is one of those phytosterols (plant sterins) with a chemical structure similar to that of cholesterol. It is a white waxy powder with a characteristic smell. Beta-sitosterol is widespread in the plant world. It is a common compound inside vegetable oils, nuts, avocados and prepared foods such as salad dressings. There were successful trials to treat benign prostate enlargement with it. Besides, it proved to be beneficial for regulating the presence of cholesterol in the blood. Since sitosterol is a precursor to an anabolic steroid, some athletes ended up with positive doping results when eating foods containing high levels of sitosterol.
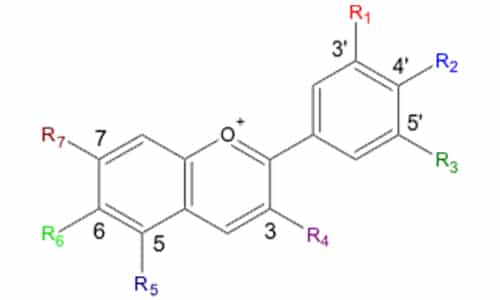
Anthocyanin
Kaempferol is a polyphenol antioxidant inside fruits and vegetables. Numerous studies describe the beneficial effects of kaempferol in reducing the risk of chronic diseases, especially cancer. Epidemiological studies show an inverse link between kaempferol intake and cancer. Kaempferol can help improve the body's antioxidant defenses against free radicals that promote the development of cancer. Significantly, kaempferol inhibits the growth of cancer cells and angiogesis and induces apoptosis of cancer cells. In addition, it appears to exert certain protective effect, thus preserving the viability of cells.
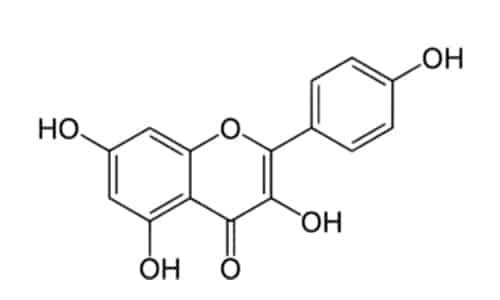
Kaempferol
Kaempferol is a polyphenol antioxidant inside fruits and vegetables. Numerous studies describe the beneficial effects of kaempferol in reducing the risk of chronic diseases, especially cancer. Epidemiological studies show an inverse link between kaempferol intake and cancer. Kaempferol can help improve the body's antioxidant defenses against free radicals that promote the development of cancer. Significantly, kaempferol inhibits the growth of cancer cells and angiogesis and induces apoptosis of cancer cells. In addition, it appears to exert certain protective effect, thus preserving the viability of cells.
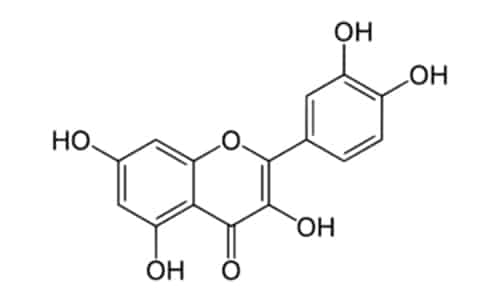
Quercetin
Quercetin is a flavonoid inside many fruits and vegetables. In appearance it is yellow crystalline powder. Quercetin occurs mainly in fruits and vegetables. For example, in apples, red grapes, cherries and green leafy vegetables. Quercetin is also in green tea and cocoa. Since quercetin occurs in the peel of fruits, it is also worth eating apples unpeeled, for instance. Quercetin strengthens the immune system and prevents the replication process of viruses. Numerous studies report on the ability of quercetin to prevent the development of viral infections. Especially in their initial stages. Quercetin is effective in even combating herpes virus. Moreover, it also proved to be effective against hepatitis B and C in different studies. In addition, quercetin does not have negative influence on the human body, since it is a completely natural plant compound. For this reason, there is no need to worry about side effects during consumption.
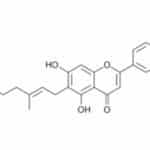
Cannflavin A, – B -C
Cannabis produces about twenty already identified flavonoids. Some of them are also in other plant varieties (such as apigenin, kampferol or quercetin). Some are unique to the Cannabis plants. Such flavonoid is cannflavin, which in fact, it is a mixture of two closely related flavonoids, CFA and CFB (8,9). Cannflavin has a significant anti-inflammatory effect. The anti-inflammatory effect of cannflavin was confirmed as early as 1985. As a matter of fact, it proved to be much stronger than aspirin. Cannflavin has equivalent potency with cannabinoids in inhibiting inflammatory prostaglandins and leukotry (7,10). These are actually the first flavonoids to have a direct inhibitory effect on two key enzymes. These enzymes are involved in the biosynthesis of proinflammatorial mediators (5-LO and PGES-1) specifically. This double inhibition can be considered as a pharmacological strategy in order to intervene in inflammatory diseases. In terms of specific targets it is especially effective in: increase in efficiency reduction of side effects
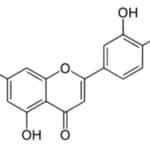
Luteolin
Luteolin is a flavon - a type of flavonoid with a yellow crystalline appearance. It is is the main yellow coloring compound obtained from the Reseda luteola plant. Luteolin has been commonly used as a natural source of paint in the 1st century BC. It is also present in the leaves, bark or flowers of many other plants. For example: celery, broccoli, green pepper, parsley, thyme, dandelion, perilla, chamomile, carrots, olive oil, peppermint, rosemary, sage and oregano. Several studies have reported physiological benefits. It protects the heart muscle and also plays a big role in relaxing other smooth muscles. It also activates the dopamine transporter, which is involved in regulating dopamine production. One study reported a 34% improvement in ovarian cancers. Another study found that it significantly reduced the risk of heart attack. Several studies also show conclusive results on its anti-inflammatory effects.
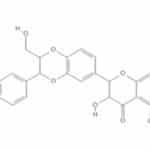
Silymarin
Silymarin is the combination of the flavonolignan silibine, silicristine and silydias in a ratio of 3:1:1. It is the main active ingredient of fig fruit. It occurs in rather larger quantities in milkweed, which is where the extractions come from. Its mechanism of action is due to the expulsion of toxins from the body. These toxins are responsible for the symptoms of many diseases, including cancer, high cholesterol, diabetes, kidney stone and gallbladder disorders. It is an antioxidant, liver protector and a detoxifier.

